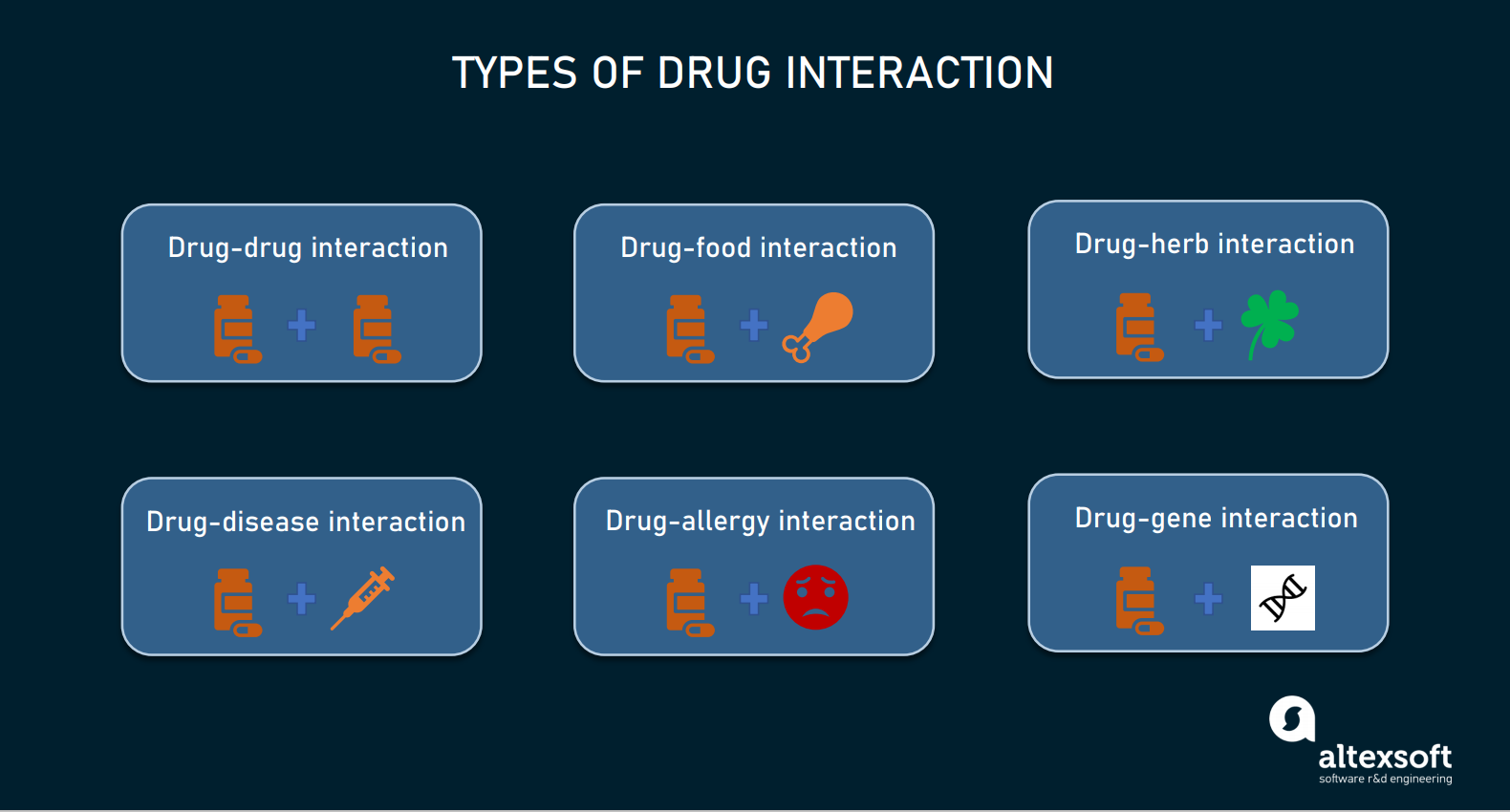
Liverpool drug interactions are emerging as a significant public health challenge. This article explores the complex interplay of medication use, demographic factors, and healthcare system limitations contributing to adverse drug reactions within the city. We examine prevalent medication combinations, the impact of polypharmacy and age, and the role of genetic predispositions in increasing interaction risks. The analysis also highlights existing public health initiatives and suggests strategies for improvement.
Data on hospital admissions due to adverse drug reactions in Liverpool, coupled with an analysis of commonly prescribed medications and their potential interactions, paints a concerning picture. The study delves into the mechanisms of these interactions, emphasizing the need for improved patient education, enhanced communication between healthcare providers, and proactive measures to mitigate risks associated with polypharmacy and genetic factors.
Drug Interactions in Liverpool: A Public Health Perspective: Liverpool Drug Interactions
Liverpool, a city with a rich history and diverse population, faces significant challenges in managing medication safety and reducing the incidence of adverse drug reactions (ADRs) stemming from drug interactions. Access to healthcare varies across different socioeconomic groups, impacting both medication adherence and the likelihood of identifying potential drug interactions. Understanding the prevalence of specific drug interactions, the influence of demographics, and the role of polypharmacy is crucial for developing effective public health strategies.
Healthcare Access and Drug Use Patterns in Liverpool

Liverpool’s healthcare system, while striving for equitable access, faces disparities in provision across its diverse population. Areas with higher levels of deprivation often exhibit lower rates of healthcare engagement, potentially leading to delayed diagnosis, suboptimal medication management, and increased risk of drug interactions. Data on specific drug use patterns within Liverpool are limited, but anecdotal evidence suggests a prevalence of polypharmacy among older adults and those with multiple chronic conditions.
This, coupled with potential barriers to accessing appropriate healthcare, contributes to the complexity of managing drug interactions within the city.
Common Medications and Potential Interactions in Liverpool
Five commonly prescribed medications in Liverpool and their potential interactions include: Paracetamol (acetaminophen), often interacting negatively with warfarin (an anticoagulant); Statins (for cholesterol), potentially interacting with grapefruit juice; Metformin (for diabetes), sometimes interacting adversely with certain diuretics; Antibiotics (like penicillin), which can interact with oral contraceptives; and antidepressants (SSRIs), that may interact with certain pain relievers. Understanding the mechanisms of these interactions is vital for healthcare professionals to provide safe and effective care.
| Medication 1 | Medication 2 | Type of Interaction | Potential Consequences |
|---|---|---|---|
| Paracetamol | Warfarin | Increased bleeding risk | Increased risk of bruising, nosebleeds, or more serious bleeding events. |
| Statins | Grapefruit Juice | Increased statin levels | Increased risk of muscle pain (myalgia) and liver damage. |
| Metformin | Loop Diuretics | Increased risk of lactic acidosis | A serious metabolic complication characterized by the buildup of lactic acid in the blood. |
| Penicillin | Oral Contraceptives | Reduced contraceptive efficacy | Increased risk of unintended pregnancy. |
| SSRIs | NSAIDs (e.g., ibuprofen) | Increased bleeding risk | Increased risk of gastrointestinal bleeding. |
Age and Demographics in Drug Interactions
Age significantly impacts drug metabolism and interaction risk. Older adults, with their often slower metabolism and increased prevalence of comorbidities, are particularly vulnerable. Younger populations may experience different interaction profiles due to varying metabolic rates and lifestyle factors. Data on specific interaction prevalence across age groups in Liverpool is needed, but existing research suggests a higher risk among the elderly.
A bar chart visualizing this would show the relative risk of drug interactions across different age brackets (e.g., 18-30, 31-50, 51-70, 70+), with the 70+ group exhibiting the highest risk. The chart would clearly illustrate the increasing risk associated with age.
Impact of Polypharmacy on Drug Interactions, Liverpool drug interactions
Polypharmacy, the concurrent use of multiple medications, is prevalent among older Liverpool residents and those with chronic conditions. This increases the likelihood of drug interactions. Common problematic combinations include the concurrent use of multiple sedatives, anticoagulants with NSAIDs, and certain antihypertensives with diuretics. Healthcare providers in Liverpool utilize medication reviews, electronic prescribing systems, and collaborative care models to mitigate polypharmacy risks.
The Role of Genetic Factors in Drug Interactions

Genetic variations significantly influence drug metabolism and interaction risk. Individuals with specific genetic polymorphisms may metabolize drugs differently, leading to either increased efficacy or toxicity. Genetic testing could personalize medication selection and dosing, minimizing interactions. While comprehensive data on Liverpool’s genetic landscape regarding drug metabolism is limited, research on common polymorphisms like CYP2D6 and CYP2C9 would be valuable in improving drug safety.
- CYP2D6: Influences the metabolism of many antidepressants and antipsychotics.
- CYP2C9: Affects the metabolism of warfarin and some NSAIDs.
- UGT2B7: Plays a role in the metabolism of several drugs, including irinotecan (a cancer drug).
Public Health Initiatives and Educational Campaigns
Liverpool’s public health initiatives include medication safety awareness programs targeting vulnerable populations. Educational campaigns could focus on medication reconciliation, the importance of informing healthcare providers about all medications, and the recognition of potential side effects. Improving public awareness through community outreach programs and utilizing diverse communication channels would significantly enhance medication safety.
Healthcare System Challenges and Solutions
Challenges include communication gaps between healthcare providers, fragmented care settings, and inconsistent patient education. Solutions include implementing electronic health records, strengthening inter-professional collaboration, and enhancing patient education materials. Improved patient adherence could be achieved through personalized medication plans and support services.
Future Directions and Research Needs
Further research is needed on the specific drug interaction profiles within Liverpool’s diverse population, considering socioeconomic factors and genetic variations. Utilizing technological advancements, such as AI-powered drug interaction checkers and personalized medicine approaches, could improve drug safety and patient outcomes. Investment in data collection and analysis would be crucial for developing targeted interventions.
Do not overlook the opportunity to discover more about the subject of quand joue manchester city.
Addressing the escalating problem of Liverpool drug interactions requires a multi-pronged approach. Improved patient education, streamlined communication within the healthcare system, and the strategic implementation of genetic testing can significantly reduce adverse drug events. Further research focusing on Liverpool’s unique demographic and healthcare landscape is crucial to developing targeted interventions and ensuring better patient outcomes. The ultimate goal is to create a safer medication environment for all Liverpool residents.